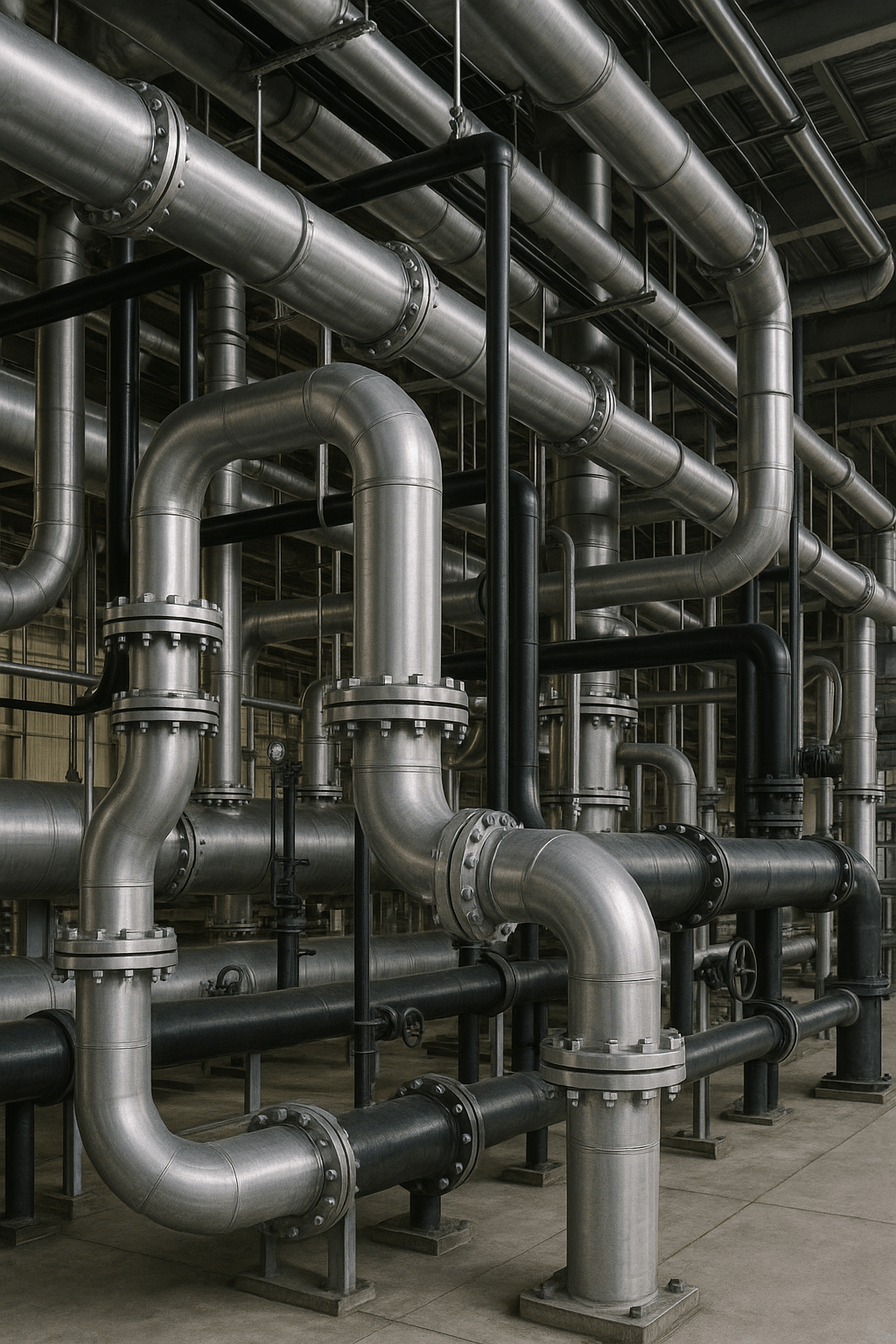
In Scandinavian manufacturing, industrial piping systems form the backbone of essential utilities—handling water, chemicals, steam, gas, and more. This guide covers everything from fluid types and pipe materials to design, installation, and maintenance best practices.
Fluids Handled in Industrial Piping Systems
Piping networks carry a range of fluids with unique properties:
- Liquids: water (cooling/heating), corrosive chemicals, slurries, petroleum
- Gases: natural gas, steam, compressed/inert gases
Industrial Pipe Materials (and why they matter)
Material choice depends on fluid characteristics and environment:
- Carbon and stainless steel: for high-pressure, high-temperature or sanitary applications
- Plastic pipes (PVC, PE, PP): lightweight, corrosion-resistant options
- Copper: heat exchangers and thermal utilities
Key Components in an Industrial Piping System
Beyond pipes, systems include:
- Fittings: elbows, tees, flanges for routing fluids
- Valves: ball, gate, globe valves for flow control
- Pumps & Compressors: to manage fluid pressure and flow
Design & Safety Considerations
Key design criteria include:
- Temperature & pressure: matching SDR and pipe material
- Corrosivity & stress analysis: to withstand environmental and operational loads
- Seismic support: critical in Scandinavia’s northern zones
- Future access: layout should allow easy maintenance
Installation Techniques That Ensure Safety
Proper joining is vital:
- Welding: TIG/MIG by certified welders
- Flanges: torque to specified bolt preload
- Threaded fittings: clean, aligned threading
Maintenance & Inspection Practices
Proactive strategies include:
- Pressure testing and non-destructive testing (NDT)
- Visual inspections for leaks, corrosion, vibration signs
- Thermal imaging to detect heat issues
The Piping Engineer’s Role
Piping engineers do more than draw diagrams—they specify materials, ensure standards (ASME, API), oversee commissioning, and support operations.
Typical Industrial Piping Scenarios
Among common use cases are:
- Process piping: chemicals, refineries, power plants
- Utility piping: steam, water, compressed air
- Fire protection: sprinkler and hydrant systems
Conclusion
Well-designed industrial piping systems—using correct materials, installation, and maintenance—are vital for Scandinavian industries. Integrating smart sensors and sustainable materials will define the next generation of piping systems.
Read more about energy-saving pipe materials and plastic pipe modernization.
Explore ASME code details on ASME.org and API standards at API.org.


